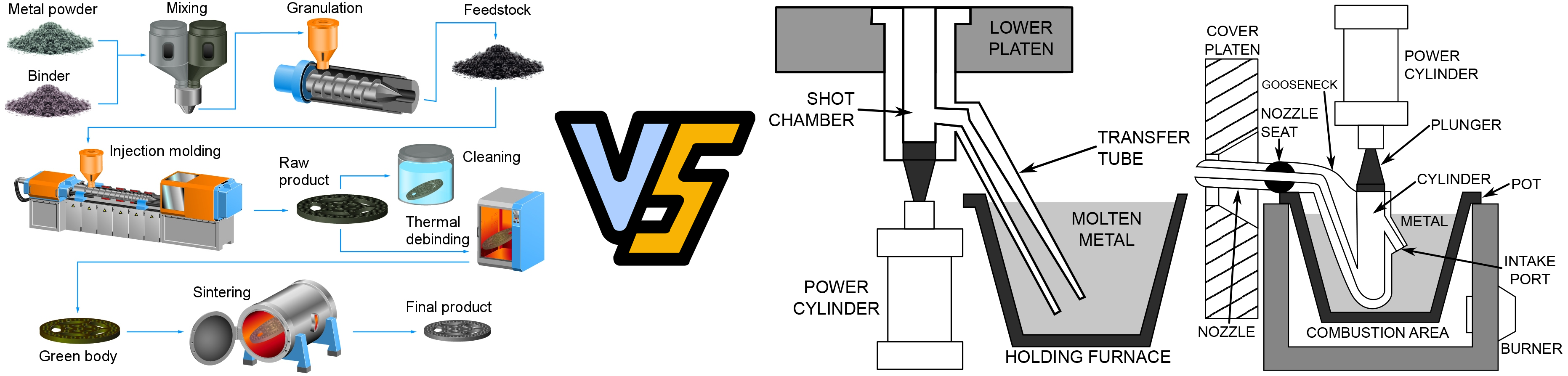
In modern manufacturing, Metal Injection Molding (MIM) has become an important technology for producing highly complex and high-precision metal parts. MIM technology combines metal powder with plastic to produce complex metal parts through an injection molding process. Due to its excellent design freedom, good mechanical properties and efficient production capacity, MIM is widely used in various industries such as automotive, medical, aerospace, etc.

Metal injection molding can produce a variety of high-performance, complex geometric parts without additional processing. Due to the high density of MIM parts, its performance is comparable to other manufacturing methods. The flexibility of material selection is high, and the same equipment can be produced with different metal materials. In addition, the MIM process can be applied to a wide variety of metals. Metal powders with various chemical compositions, particle sizes and shapes will determine the final MIM part performance.
Our MIM materials are divided into the following categories:
1. Stainless steel
1.1 Features and advantages
Stainless steel is one of the most commonly used materials in MIM, mainly due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The alloy composition of stainless steel can effectively prevent oxidation and corrosion, and is particularly suitable for environments that require corrosion resistance. Common types of stainless steel include 304 and 316 stainless steel:
304 stainless steel: Also known as 18/8 stainless steel, it contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel. It has good corrosion resistance, processability and formability, and is widely used in household goods, kitchen equipment and other fields.
316 stainless steel: Contains 16% chromium, 10% nickel and 2% molybdenum, which has stronger corrosion resistance than 304 stainless steel and is particularly suitable for use in marine environments and chemical industries.
1.2 Application areas
Stainless steel MIM parts are used in the automotive industry to manufacture complex engine parts and decorative parts; in the medical field, they are used to manufacture surgical instruments and implants; in the consumer electronics field, they are used for the housing and internal components of high-end electronic products.
2. Carbon steel
2.1 Features and advantages
Carbon steel is an economical and practical MIM material, whose main components are iron and carbon. The hardness, strength and toughness of carbon steel can be controlled by adjusting the carbon content and other alloying elements. Common carbon steels include 1010 and 1020, etc.:
1010 carbon steel: contains about 0.1% carbon and is suitable for applications requiring high weldability and formability.
1020 carbon steel: contains about 0.2% carbon, has high strength and hardness, and is suitable for structural parts that require a certain strength.
2.2 Application areas
Carbon steel MIM parts are mostly used in automotive parts, mechanical structural parts, and tool components. Its cost-effectiveness makes it excel in many standardized and high-volume applications.
3. Tool steel
3.1 Features and advantages
Tool steels are high-performance steels used to make tools and molds. They usually have high hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Common types of tool steels include D2 and M2:
D2 tool steel: contains high carbon and high chromium, has good wear resistance and compression resistance, and is suitable for making high-wear-resistant cutting tools.
M2 tool steel: is a high-speed steel containing tungsten and molybdenum, suitable for high-temperature cutting tools and molds.
3.2 Applications
Tool steel MIM parts are widely used in cutting tools, mold making, and high-precision mechanical parts. They are able to maintain good performance in high-strength and high-wear environments.
4. Titanium alloys
4.1 Features and advantages
Titanium alloys have excellent strength-to-weight ratios and are often used in applications that require high strength and low weight. The most common titanium alloy is Ti-6Al-4V, which consists of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium:
Ti-6Al-4V: has excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance, suitable for high-performance structural parts.
4.2 Applications
Titanium alloy MIM parts are widely used in the aerospace field, medical devices (such as artificial joints and dental implants), and high-performance sports equipment. Its high strength and low weight characteristics make it an ideal choice for these applications.
5. High-temperature alloys
5.1 Features and advantages
High-temperature alloys, such as Inconel and Hastelloy, are designed for use in extremely high-temperature environments. They usually contain nickel, chromium and other alloying elements to provide excellent high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance:
Inconel: has excellent high-temperature oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance, and is often used in gas turbines and high-temperature chemical processing equipment.
Hastelloy: Mainly used in chemical processing and petrochemical fields, its corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability are excellent.
5.2 Application Fields
High-temperature alloy MIM parts are widely used in the aerospace, energy and chemical processing industries. They are able to maintain stable performance under extreme working conditions.
6. Aluminum Alloys
6.1 Features and Advantages
Aluminum alloys are less used in MIM, but they still have their market in applications that require lightweighting. Aluminum alloys have excellent mechanical properties, good formability and corrosion resistance. Common aluminum alloy types include 6061 and 7075:
6061 aluminum alloy: contains silicon and magnesium, has good processability and mechanical properties, and is suitable for structural applications.
7075 aluminum alloy: contains zinc, has higher strength, and is often used in aerospace and military applications.
6.2 Application Areas
Aluminum alloy MIM parts are commonly used in aerospace, automotive and high-performance sports equipment. They offer light weight and high strength, suitable for applications that require weight reduction.
The core of MIM technology lies in its ability to combine metal powder with plastic to produce complex-shaped metal parts through an efficient injection molding process. Selecting the appropriate MIM material is critical to ensuring the performance of the part and meeting application requirements. From stainless steel to titanium alloy, each material has its own unique properties and application areas. When selecting MIM materials, factors such as part strength, corrosion resistance, wear resistance and cost need to be considered comprehensively.
MIM Material Applications
| Material Category | Material Type | Characteristics | Application |
| Stainless steel | 316L | Corrosion resistance | Horology parts, electronic component |
| Stainless steel | 304 | High strength | Electronic parts, micro-gears |
| Stainless steel | 420 | High strength | Pneumatic machinery, cutlery, tools |
| Stainless steel | 440C | Friction resistance, corrosion resistance | Hand tools, sporting equipment |
| Stainless steel | 17-4 PH | Corrosion resistance and strength | Medical, dental, surgical parts |
| Stainless steel | P.A.N.A.C.E.A | Non-magnetic | Electronics, |
| Fe-based alloy | 4605 | Exceptional strength, good ductility | Consumer products, hand tools |
| Fe-based alloy | Fe3%Si | High electrical resistance | Electrical parts |
| Fe-based alloy | Fe50%Ni | High permeability | Electrical parts |
| Fe-based alloy | Fe50Co | High permeability | Micro-motor |
| Copper | Copper alloy | Thermal & electrical conductivity | Heat conduction, electric conduction |
| Hard alloy | Nickel alloy | electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance | Electrical parts, wristwatch parts |
| Titanium | Ti-6Al-4V | Corrosion resistance, light weight | Medical parts |
| Special alloy | ASTM F15 (Kovar) | Controlled expansion | Splitter, micro-electronic parts |
| Special alloy | ASTM F75 | Bio-compatibility, wear resistance | Medical, orthopedics, dental parts |
| Special alloy | ASTM F1537 | Bio-compatibility, corrosion resistance | Medical parts |
We have a wide range of MIM materials for you to choose
|
Brand |
Phase structure |
Magnetism |
Heat treatment |
Application |
|
304L |
Austenite |
weak magnetism |
No hardening effect |
Internal structure and appearance, lens ring protective cover/card holder |
|
316L/317L |
Austenite |
weak magnetism |
No hardening effect |
Internal structure and appearance, lens ring protective cover/card holder |
|
904L |
Austenite |
weak magnetism |
No hardening effect |
Highlight parts for smart watches |
|
P.A.N.A.C.E.A. |
Austenite |
no magnetism |
No magnetic corrosion resistance |
Circuit board bracket and nonmagnetic structural parts, lens ring protective cover |
|
310N |
Austenite |
weak magnetism |
No hardening effect |
Heat resistant for long term use 750800°C |
|
420J2 |
Martensite |
strong magnetism |
Water quenching hardening |
Wearresistant parts, various cushions, product shaftslaptops/folding screen mobile phones |
|
440C |
Martensite |
strong magnetism |
Water quenching hardening |
Wearresistant parts, various cushions, product shaftslaptops/folding screen mobile phones |
|
2507 |
Duplex |
strong magnetism |
Water quenching hardening |
Smart watch highlights |
|
174PH |
Duplex |
strong magnetism |
Precipitation hardening |
Various structural parts/connectors and terminal ports |
|
Brand |
Phase structure |
Heat treatment |
Application |
|
Fe |
Moderate Magnetic |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts, requiring various antirust treatments/inductor components |
|
(SAE1010) |
High magnetic induction |
||
|
Fe2Ni |
Moderate Magnetic |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts require various antirust treatments |
|
Fe4Ni |
Moderate Magnetic |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts require various antirust treatments |
|
Fe8Ni |
Moderate Magnetic |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts require various antirust treatments |
|
Fe50Ni |
High magnetic permeability |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts require various antirust treatments |
|
FeSi3 |
High magnetic permeability |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts require various antirust treatments |
|
Low Alloy |
Moderate Magnetic |
Hardening according to carbon content |
Internal structural parts, requiring various antirust treatments/inductor components |
|
((Low content of nonferrous elements)) |
High magnetic induction |
|
Brand |
Phase structure |
Heat treatment |
Application |
|
Fe50Co |
No magnetic conductivity |
Annealing softening improves toughness |
Connector and terminal port/EMC shielding |
|
ASTM F75 |
No magnetic conductivity |
Annealing softening improves toughness |
Circuit board bracket and nonmagnetic structural parts, lens ring protective cover |
|
Inconel 718 |
No magnetic conductivity |
Annealing softening improves toughness |
Internal structural parts such as connectors and terminal ports |
|
WNiFe |
Low Magnetic |
Dehydrogenation improves toughness |
Various counterweights and vibration plates |
|
Cu |
Nonmagnetic |
Dehydrogenation improves toughness |
Various heat dissipation and EMC screen wall cover designs |
|
WCu |
Nonmagnetic |
Dehydrogenation improves toughness |
Various heat dissipation and low deformation and fast heat dissipation are required |
|
Ti (TA1) |
Nonmagnetic |
Dehydrogenation improves toughness |
Especially for contact with human body |
|
Ti6Al4V (TC4) |
Nonmagnetic |
Dehydrogenation improves toughness |
Especially for contact with human body |
|
High strength steel THOR |
Nonmagnetic |
Precipitation hardening |
Axis |
The above are our existing MIM materials, if you can't find the raw materials that meet your requirements, please let us help you.

Share:
Our MIM Materials
Custom Ceramic Parts: Precision Solutions for High-Performance Materials