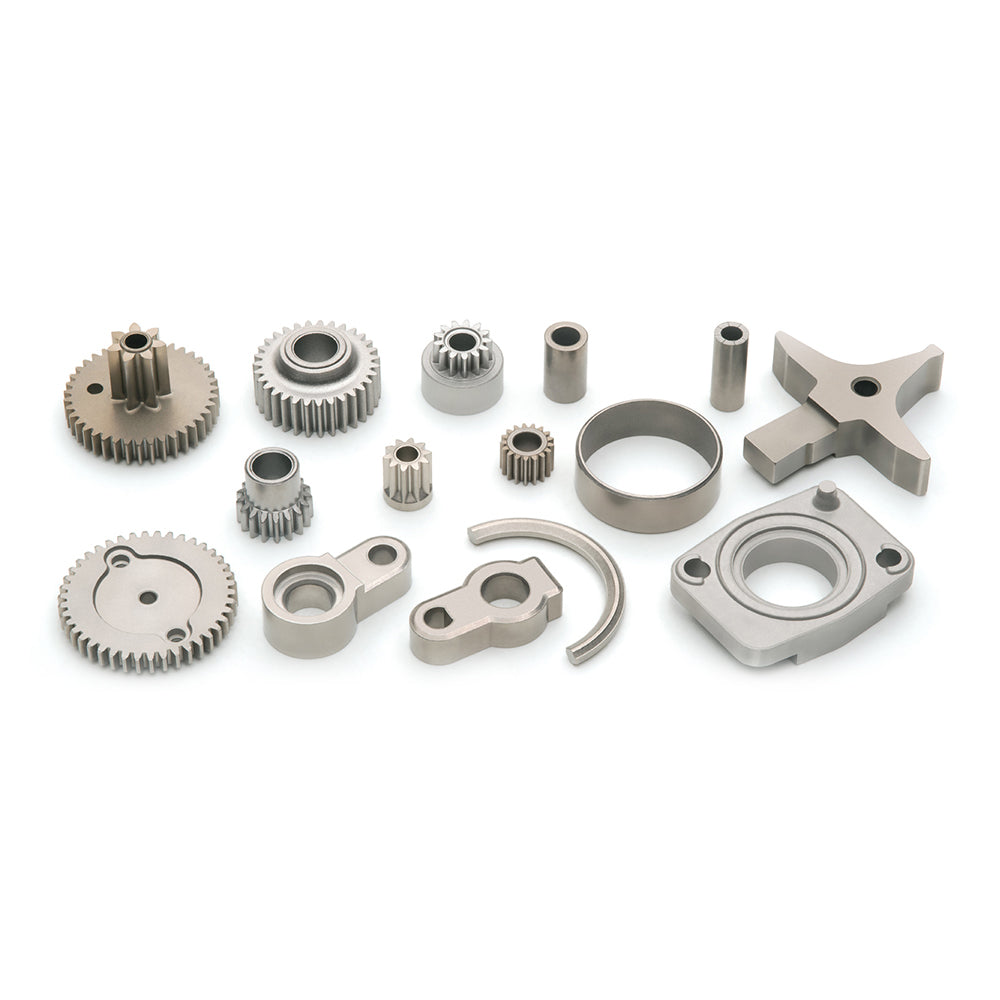
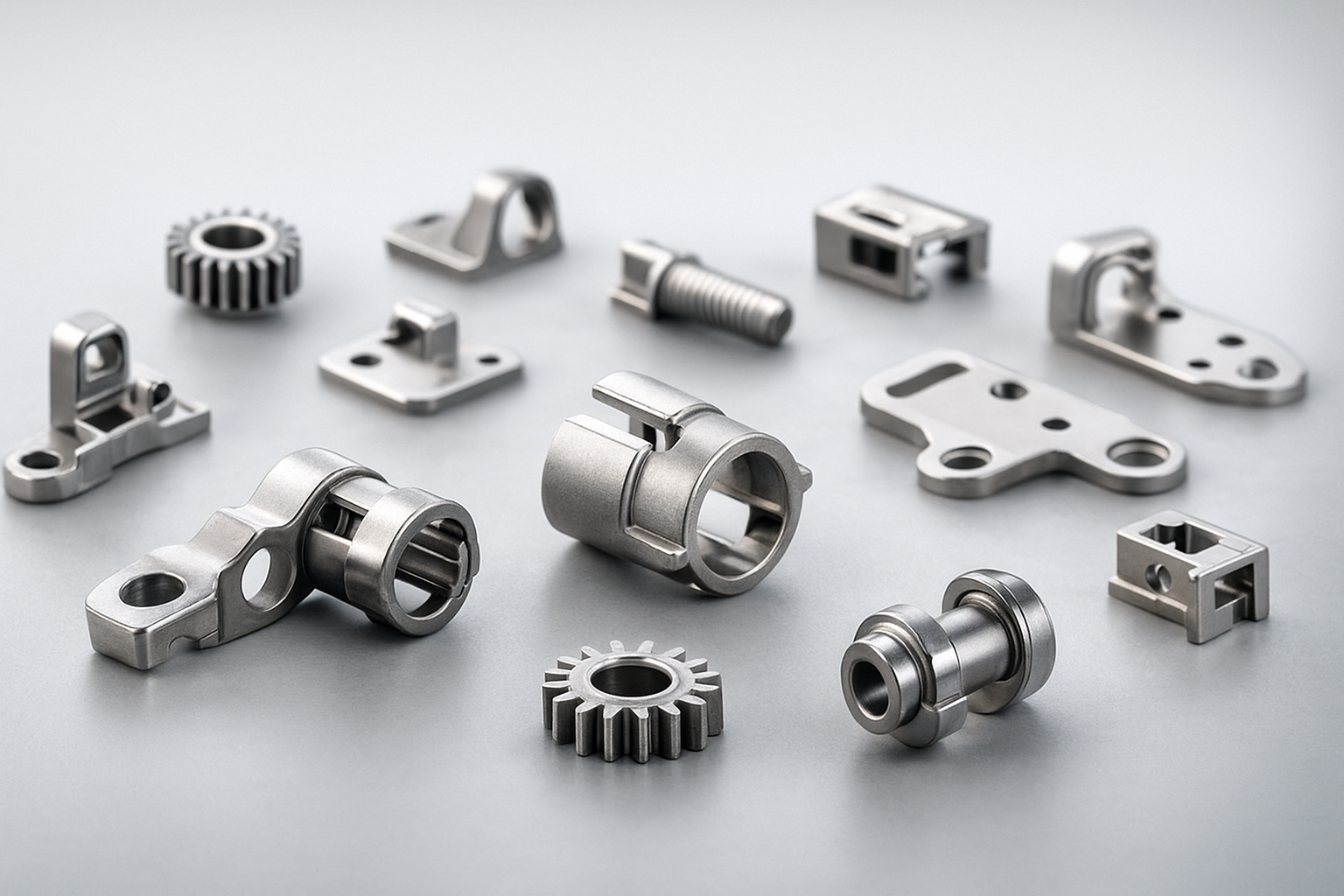
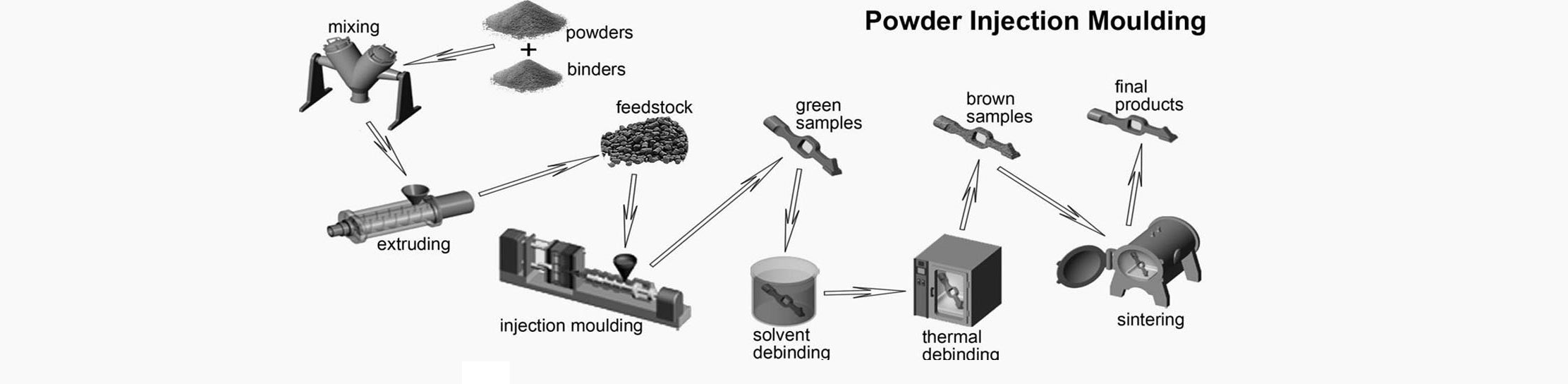
MIM Process
MIM works like any other injection molding process -- a powder metal is combined with a bonding material and then injected into a mold, where it is molded and cured. The end result is metal parts. The process is ideal for the short - and long-term production of metal parts, especially those with smaller sizes and finer properties. The following is a detailed description of the MIM process:
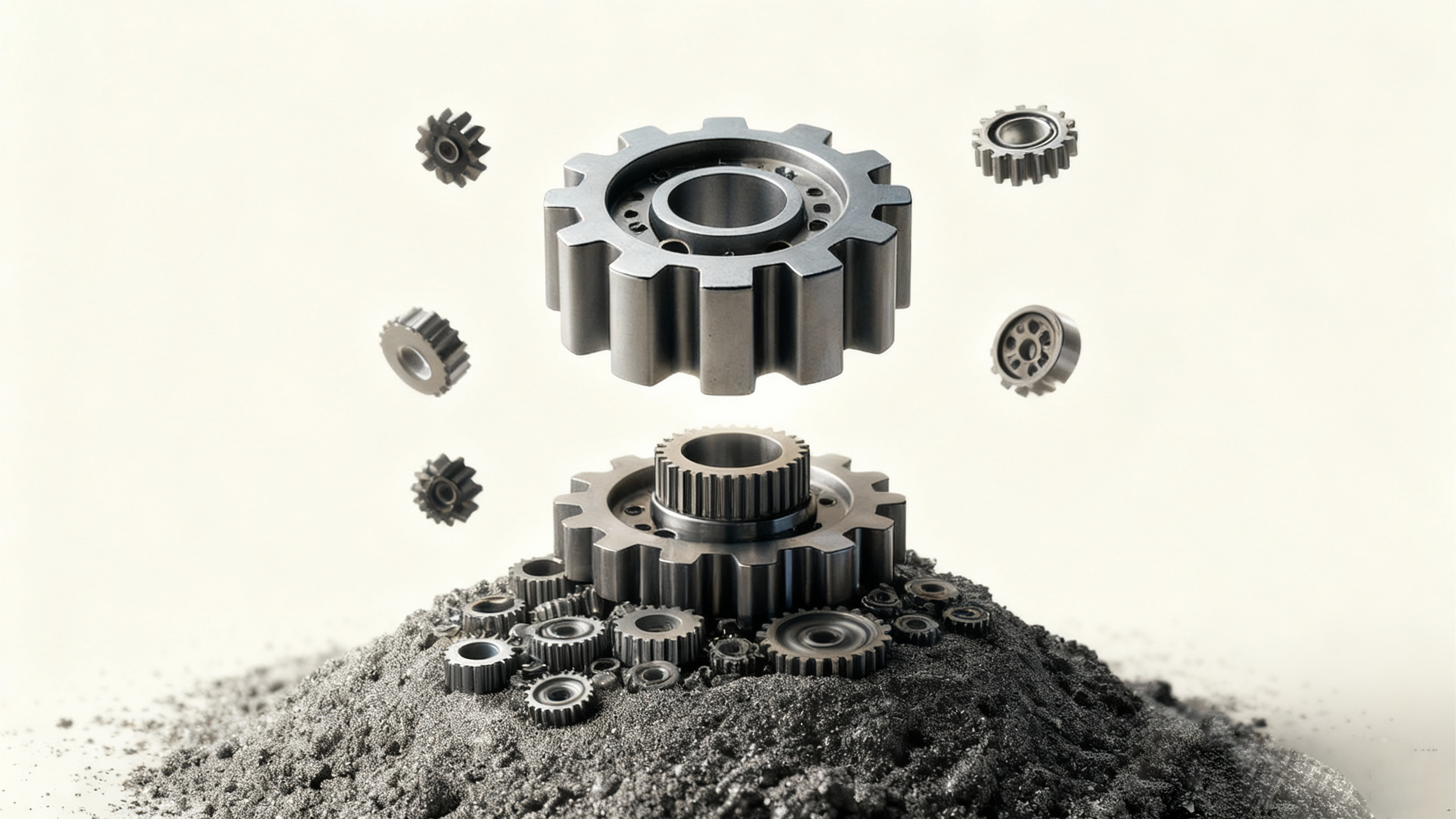
 1. Mixing and granulating: The first step in the metal injection molding process is to determine the materials and raw materials that will be used to make the parts. (For more information on the scope of the material, see the section near the bottom of this article.) Usually, this consists of fine powder metal - a powder that is fine enough to produce the necessary characteristics. Once the metal powder is identified, it is mixed with a thermoplastic adhesive (usually 40% of the total raw material), heated to bind the metal particles to the adhesive, and then fed into an injection molding machine.
1. Mixing and granulating: The first step in the metal injection molding process is to determine the materials and raw materials that will be used to make the parts. (For more information on the scope of the material, see the section near the bottom of this article.) Usually, this consists of fine powder metal - a powder that is fine enough to produce the necessary characteristics. Once the metal powder is identified, it is mixed with a thermoplastic adhesive (usually 40% of the total raw material), heated to bind the metal particles to the adhesive, and then fed into an injection molding machine.
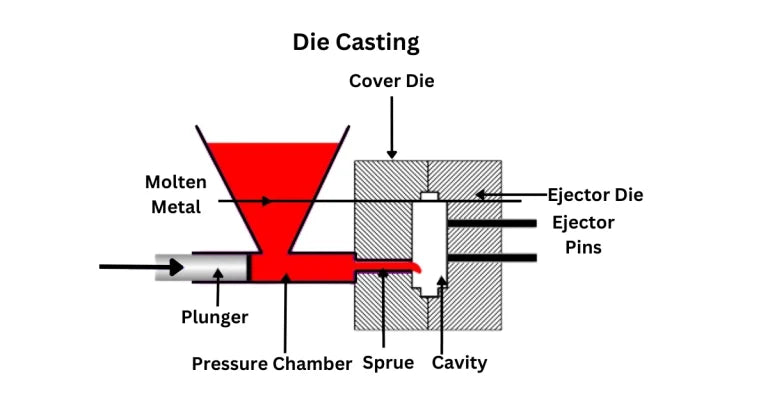
2. Molding: The next step is the molding process, where the material is reheated and then injected into the machine for the molding process, which is where the parts are created.
3. Adhesive removal: After the part ejection, the next step is to remove the adhesive. This is because the final portion is 20% larger than the expected final portion. Therefore, in order to get it to its actual size, the adhesive needs to be removed.
4. Sintering: The final step of the process involves sintering, in which the remaining adhesive is removed from the part and the metal is melted to form the part, the end result being a final part of a final shape or near final shape. Further post-sintering operations may also be required to properly create the final part, which may add some further steps and process complexity.









Share:
MIM Process Advantages and Limitations for Automotive, Medical, Dental, Consumer Electronics, Industrial And Consumer Products
Production Equipment for Metal Injection Molding, Professional Machine, Precision Tools for High-Quality MIM Services